Recent Developments in Azole Compounds as Antitubercular Agent
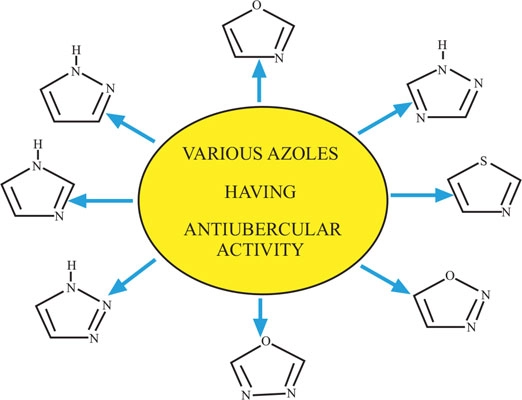
Tuberculosis (TB) is a global health disaster and is a wide-reaching hitch. The improper use of antibiotics in chemotherapy of TB patients led to the current problem of tuberculosis therapy which gives rise to Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) strains. Nitrogen heterocycles including azole compounds are an important class of therapeutic agent with electron-rich property. Azole-based derivatives easily bind with the enzymes and receptors in organisms through noncovalent interactions, thereby possessing various applications in medicinal chemistry. Research on azoles derivatives have been expansively carried out and have become one of the extremely active area in recent years and the progress is quite rapid. A genuine attempt to review chemistry of azoles and to describe various azole-based compounds synthesized in the last two decades having promising antitubercular potential is described in the present article. It is hopeful that azole compounds may continue to serve as an important direction for the exploitation of azole-based antitubercular drugs with better curative effect, lower toxicity, less side effects, especially fewer resistances and so on.
Publisher URL: http://www.eurekaselect.com/node/163190/article/recent-developments-in-azole-compounds-as-antitubercular-agent
DOI: 10.2174/1570193x15666180622144414
Keeping up-to-date with research can feel impossible, with papers being published faster than you'll ever be able to read them. That's where Researcher comes in: we're simplifying discovery and making important discussions happen. With over 19,000 sources, including peer-reviewed journals, preprints, blogs, universities, podcasts and Live events across 10 research areas, you'll never miss what's important to you. It's like social media, but better. Oh, and we should mention - it's free.
Researcher displays publicly available abstracts and doesn’t host any full article content. If the content is open access, we will direct clicks from the abstracts to the publisher website and display the PDF copy on our platform. Clicks to view the full text will be directed to the publisher website, where only users with subscriptions or access through their institution are able to view the full article.


