Neoisoliquiritin exerts tumor suppressive effects on prostate cancer by repressing androgen receptor activity
Background
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in men in both developed and developing countries. Androgens and the androgen receptor (AR) play predominant roles in the progression of PCa. Neoisoliquiritin (NEO) belongs to the class of licorice (Glycyrrhiza) flavonoids, which have a variety of biological activities including anti-depressant, anti-tumor-promoting, and anti-inflammation properties. Licorice root has cancer chemopreventive effects and has been given to PCa patients as an ingredient of PC-SPES, a commercially available combination of eight herbs. Therefore, we determined if NEO can suppress the proliferation of PCa cells.
Purpose
We investigated whether and how NEO exerts its anti-neoplastic activity against PCa.
Methods
The Cell Counting Kit 8 and flow cytometry were used to evaluate the effects of NEO on the proliferation and cell cycle progression of AR-dependent (LNCaP) and AR-independent (PC3) PCa cells. RNA sequencing was employed to examine the genome-wide changes in responsiveness to NEO in LNCaP cells. Quantitative PCR, Western blotting, docking, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and dual-luciferase reporter assays were conducted to determine the mechanism of action of NEO and its potential cross-talk with AR. A LNCaP xenograft nude mouse model was used to determine the inhibitory effects of NEO on AR-dependent PCa tumors in vivo.
Results
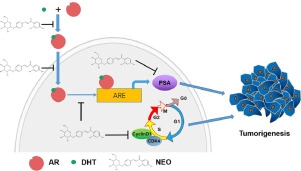
NEO inhibited LNCaP cell proliferation in vitro by inducing G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Conversely, NEO treatment had no effect on PC3 cells. Transcriptomic analysis indicated that AR signaling might be the key target of NEO in preventing PCa. NEO regulated AR-mediated cell growth suppression and AR-sensitized cell cycle arrest in LNCaP cells. NEO also blocked several key steps in the AR signaling pathway, including proposed targeting to the ligand binding pocket of AR by computer modeling, modulating AR–androgen response element DNA-binding activity, inhibiting the expression and transcriptional activity of AR, and suppressing downstream AR signaling.
Conclusions
NEO negatively regulates AR expression and activity, thus supporting the tumor suppressive role for NEO in AR-dependent PCa.
Publisher URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711321000568
DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153514
Keeping up-to-date with research can feel impossible, with papers being published faster than you'll ever be able to read them. That's where Researcher comes in: we're simplifying discovery and making important discussions happen. With over 19,000 sources, including peer-reviewed journals, preprints, blogs, universities, podcasts and Live events across 10 research areas, you'll never miss what's important to you. It's like social media, but better. Oh, and we should mention - it's free.
Researcher displays publicly available abstracts and doesn’t host any full article content. If the content is open access, we will direct clicks from the abstracts to the publisher website and display the PDF copy on our platform. Clicks to view the full text will be directed to the publisher website, where only users with subscriptions or access through their institution are able to view the full article.


