Real-time tracking lysosomal pH changes under heatstroke and redox stress with a novel near-infrared emissive probe
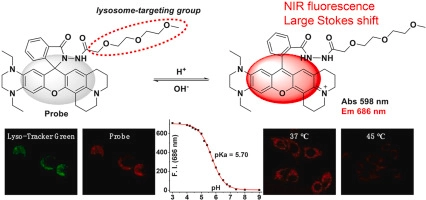
Lysosomes are important subcellular organelles with acidic pH. The change of lysosomal pH can affect the normal function and activity of cells. To conveniently detect and visualize lysosomal pH changes, we designed herein a novel fluorescent probe NIR-Rh-LysopH. The probe is based on a Rhodamine 101 derivative, which was modified to include a fused tetrahydroquinoxaline ring to obtain near-infrared fluorescence and a methylcarbitol moiety to locate the lysosome. Based on the proton-induced spirolactam ring-opening mechanism, NIR-Rh-LysopH showed rapid, selective, sensitive, and reversible near-infrared fluorescence responses around 686 nm (Stokes shift 88 nm) with a pKa value of 5.70. From pH 7.4 to 4.0, about 285 folds of fluorescence enhancement was observed. Cell experiments showed that NIR-Rh-LysopH has low cytotoxicity and excellent lysosome-targeting ability. Moreover, NIR-Rh-LysopH was applied successfully to track lysosomal pH changes induced by drugs (such as chloroquine and dexamethasone), heatstroke, and redox stress. Thus, NIR-Rh-LysopH is very promising for conveniently tracking lysosomal pH changes and studying the related life processes.
Publisher URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0039914021001053
DOI: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122184
Keeping up-to-date with research can feel impossible, with papers being published faster than you'll ever be able to read them. That's where Researcher comes in: we're simplifying discovery and making important discussions happen. With over 19,000 sources, including peer-reviewed journals, preprints, blogs, universities, podcasts and Live events across 10 research areas, you'll never miss what's important to you. It's like social media, but better. Oh, and we should mention - it's free.
Researcher displays publicly available abstracts and doesn’t host any full article content. If the content is open access, we will direct clicks from the abstracts to the publisher website and display the PDF copy on our platform. Clicks to view the full text will be directed to the publisher website, where only users with subscriptions or access through their institution are able to view the full article.


